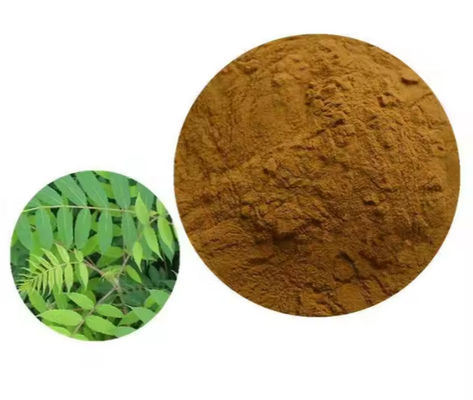
CAS NO 68915-32-2 Picrasma quassioides extract Chinese medicine and modern pharmacology
Features:
Name: Picrasma quassioides extract
CAS NO.:68915-32-2
Place of Origin: China (Mainland)
Grade Standard: Pharmaceutical Grade
| Item |
Test Result |
| Appearance |
Brown-Yellow Powder
|
| Assay |
10:1(TLC) |
Picrasma quassioides, commonly known as Kumu, is a plant belonging to the Simaroubaceae family. Its extract has been studied in both traditional Chinese medicine and modern pharmacology for various biological activities. The main efficacies of Kumu extract are as follows:
1. Anti-inflammatory Effects
Kumu extract shows significant anti-inflammatory properties, capable of inhibiting inflammatory mediators such as prostaglandin E2 and nitric oxide (NO).
2. Antibacterial and Antiviral Activities
Kumu extract exhibits inhibitory effects on various bacteria and viruses in vitro:
-
It can inhibit common pathogenic bacteria such as Escherichia coli, Staphylococcus aureus, and Candida albicans.
-
Some studies also indicate potential inhibitory effects on hepatitis B virus (HBV), although more clinical data are needed.
3. Antitumor Effects
Quassinoid compounds in Kumu, such as bruceantin and quassin, have been researched for their anticancer potential:
-
They can induce apoptosis (programmed cell death) and inhibit the proliferation of cancer cells.
-
Antitumor activities have been observed in models of liver cancer, gastric cancer, and breast cancer.
4. Antioxidant Activity
Kumu extract contains polyphenols and flavonoids that provide antioxidant effects by scavenging free radicals and inhibiting lipid peroxidation, contributing to anti-aging and cellular protection.
5. Blood Sugar Regulation and Metabolic Effects
Some studies suggest that Kumu extract can lower blood glucose levels and improve insulin sensitivity in diabetic animal models, potentially through anti-inflammatory pathways and insulin signaling modulation.
Cautions:
-
Kumu extract may have some toxicity and side effects, especially at high doses, including potential liver toxicity and gastrointestinal discomfort.
-
It is not recommended for pregnant or breastfeeding women, or children, without professional guidance.
-
Usage should ideally be under the supervision of a healthcare professional or traditional medicine practitioner.



 Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail!  Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters!
Your message must be between 20-3,000 characters! Please check your E-mail!
Please check your E-mail! 













